How FDM 3D Printing is Redefining Manufacturing and Design
In the world of manufacturing and design, the introduction of 3D printing technology has revolutionized the way products are created. Among the various 3D printing methods, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) stands out as one of the most accessible, versatile, and impactful technologies. FDM 3D printing, also known as fused filament fabrication (FFF), has changed the landscape of both manufacturing and design by offering faster, more cost-effective, and customizable solutions that were once unthinkable in traditional processes.
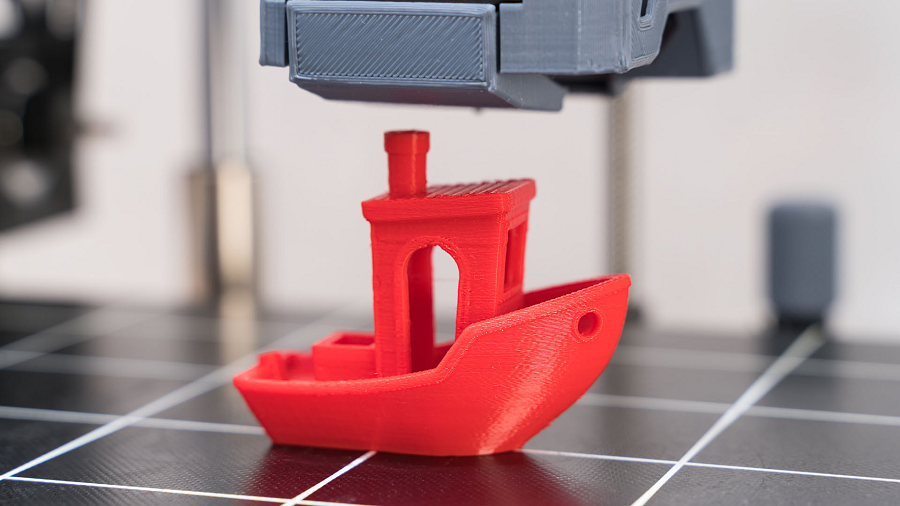
FDM is a 3D printing process that works by heating a thermoplastic filament and extruding it layer by layer to build up a 3D object. The material is deposited through a heated nozzle, which allows it to solidify as it cools, forming the desired object. This technique differs from other forms of 3D printing, such as stereolithography (SLA) or selective laser sintering (SLS), in that it is a more material-efficient, affordable, and straightforward method, which has led to its widespread adoption across various industries.
Redefining Manufacturing
The impact of FDM 3D printing on manufacturing is profound, offering numerous advantages over traditional methods such as injection molding or CNC machining. One of the primary benefits of FDM is its ability to create highly complex shapes and geometries that would be either impossible or too costly to produce with traditional methods. Manufacturers can now design intricate internal structures, lattice designs, and customized features, giving them the freedom to innovate without the constraints of traditional manufacturing techniques.
In addition, FDM 3D Printing drastically reduces lead times. Traditional manufacturing processes often require the creation of molds or tooling, which can take weeks or even months to develop. With FDM, prototypes or final products can be designed and printed in a matter of hours or days. This reduction in time to production allows manufacturers to quickly iterate and make adjustments to designs, leading to faster time-to-market and greater efficiency.
Transforming Design
The design process has also been fundamentally altered by FDM 3D printing. Designers are no longer limited by the constraints of traditional manufacturing methods, allowing for more freedom in creativity and innovation. Complex geometries, custom features, and even personalized products can be easily achieved with FDM, making it an essential tool for designers across various sectors, including automotive, fashion, and consumer goods.
One of the key features of FDM printing in design is the ability to quickly prototype and test ideas. Designers can create functional prototypes almost immediately, allowing for a more hands-on approach to testing and improving designs. This iterative process accelerates product development, reduces the risk of design flaws, and ultimately leads to better products.
The Future of FDM 3D Printing in Manufacturing and Design
As FDM 3D printing continues to evolve, the possibilities for manufacturing and design are expanding. The development of new materials, such as advanced composites and bioplastics, is opening doors to even more applications, including in industries like automotive and healthcare. Additionally, improvements in printing speed, accuracy, and material strength will only enhance the capabilities of FDM printing, enabling it to compete even more effectively with traditional manufacturing processes.
FDM 3D printing is undeniably changing the way products are designed, prototyped, and manufactured. Its ability to reduce costs, speed up production, and offer a high degree of customization has redefined the entire manufacturing landscape. As the technology continues to advance, it is likely that FDM will play an even more central role in the future of design and manufacturing, leading to more efficient, innovative, and personalized products.